Unplugging From Digital Controls to Safeguard Power Grids
Late last week, the U.S. House of Representatives passed legislation to mandate federal research on a radically ‘retro’approach to protect power grids from cyber attack: unplugging or otherwise isolating the most criticalequipment from grid operators’ digital control systems. Angus King, an independent senator from Maine whose identical bill passedthe Senate last month, says such a managed retreat from networked controls may berequired to thwart the grid’s most sophisticated online adversaries. Grid cyber experts say the Securing Energy Infrastructure Act moving through Congress isa particular testament toMichael Assante, a gifted and passionate cybersecurity expert whodied earlier this monthfrom leukaemia at the age of 48.
Read More
Store solar energy as liquid
A research group from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has made great, rapid strides towards the development of a specially designed molecule which can store solar energy for later use. These advances have been presented in four scientific articles this year, with the most recent being pub
Read More
Thin film converts heat from electronics into energy
Nearly 70 percent of the energy produced in the United States each year is wasted as heat. Much of that heat is less than 100 degrees Celsius and emanates from things like computers, cars or large industrial processes. Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have developed a thin-film system that can be applied to sources of waste heat like these to produce energy at levels unprecedented for this kind of technology.
Read More
Researchers “heal” destructive dendrite growth in lithium-metal batteries
Dendrites—branching structures that look like tree limbs—are fun to draw and good on neurons, but they’re generally best avoided in lithium-ion batteries. As ions are exchanged between the anode and cathode over several charge and discharge cycles, lithium electrodes will sometimes grow dendrites that can expand through the electrolyte that separates the anode and cathode. These dendrites can reduce the battery’s capacity, shorten the life of the battery, or even start fires as the dendrites heat up.
Read More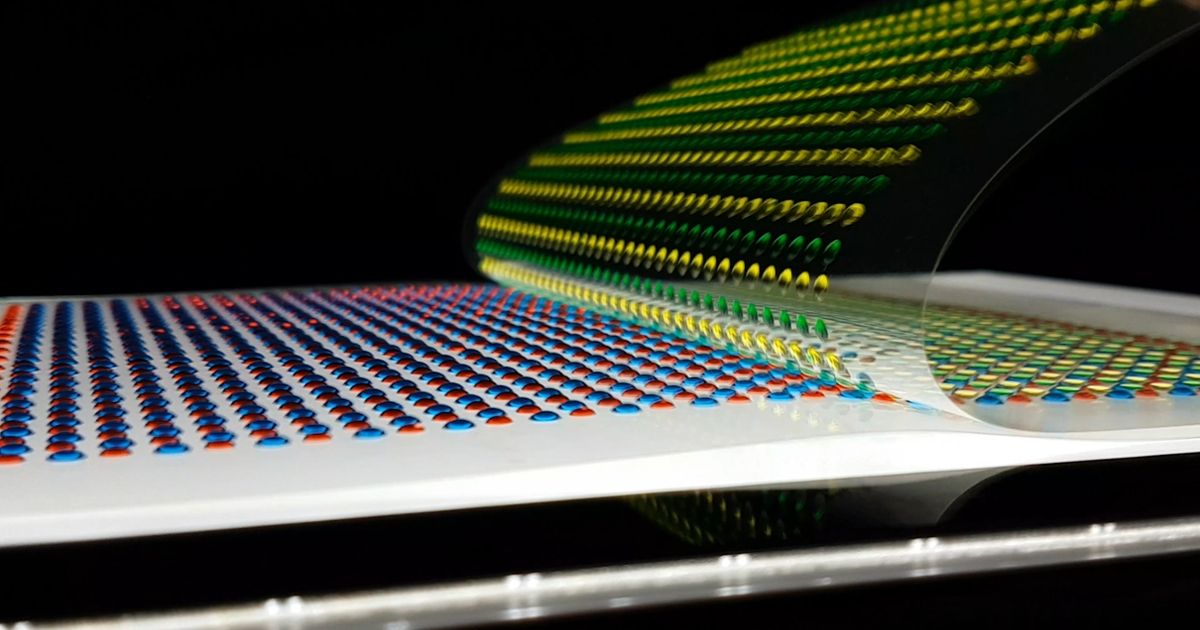
Origami-Folded Hydrogel Paper Instantly Generates 110 Volts of Electricity
Rows of small hydrogel dots are packed with positively and negatively charged ions that combine together to mimic an electric eel’s cellular structure. Printing and stacking these hydrogels produces the highest amount of voltage, while a connection to a larger contact area produces the highest current. Scientists are hoping that this system could potentially lead to a device that generates power from inside of the human body.
Read More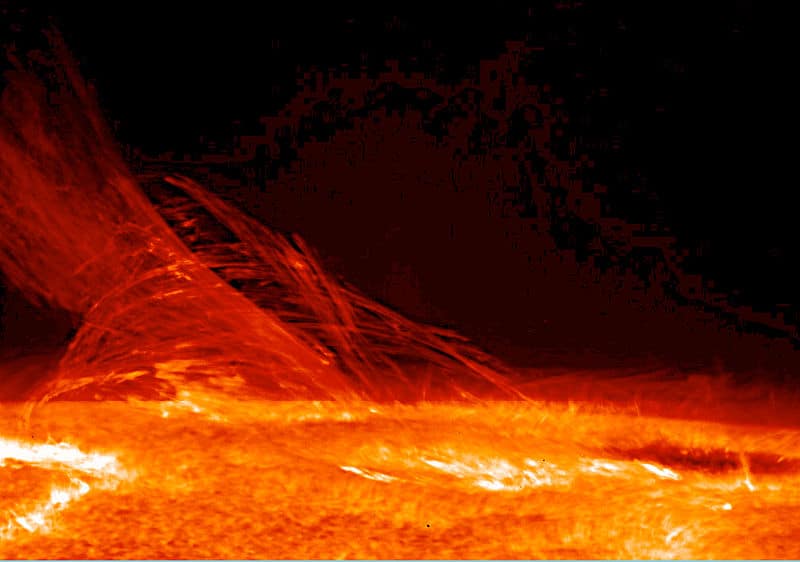
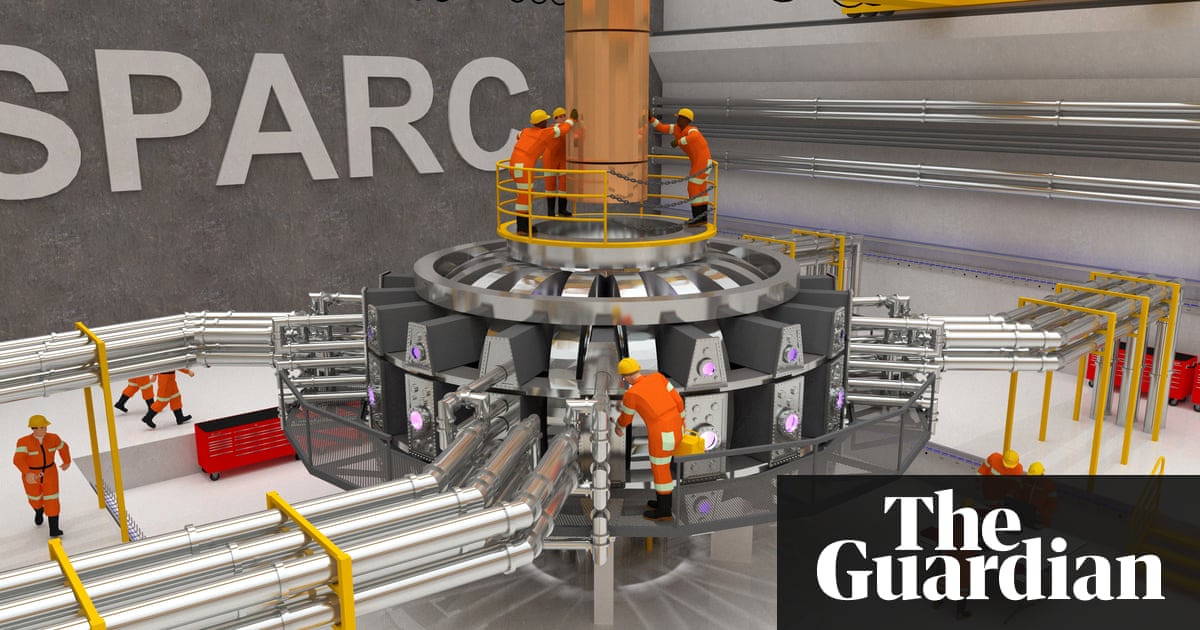
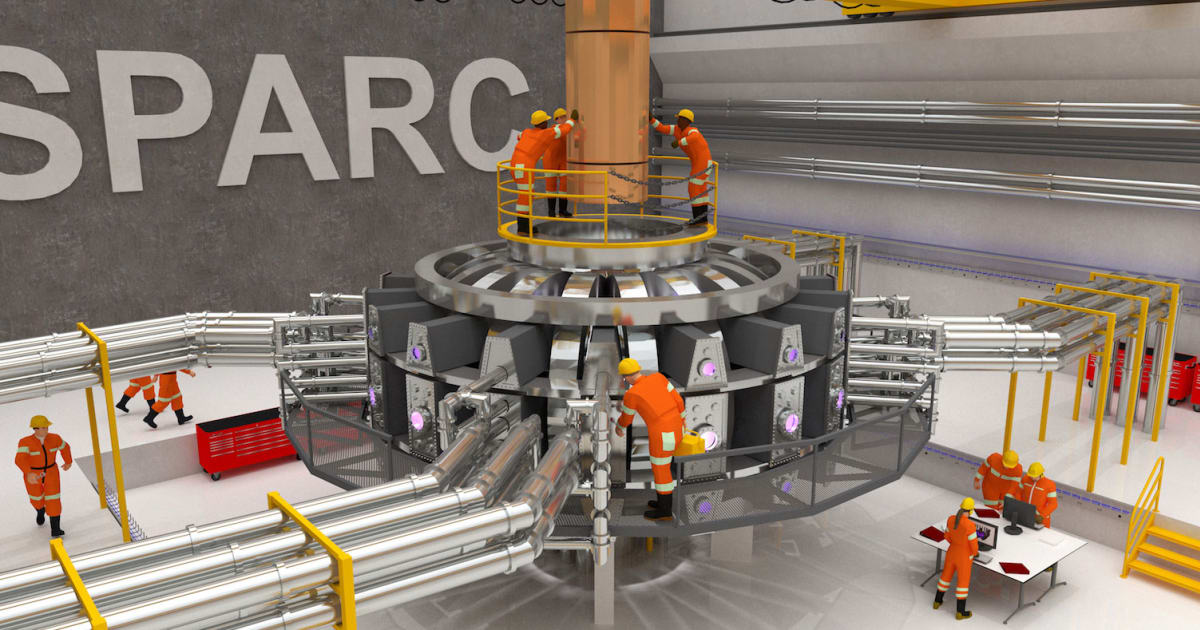
AI Researchers Aim to Crack Code on ‘Sun Energy’
Since the ’50s, scientists have chased the promise of clean energy from sun-like reactions between deuterium and tritium, the plentiful isotopes of hydrogen. This carbon-free energy, achieved at temperatures of 360 million degrees Fahrenheit, would offer a great way to heat water and, in turn, spin turbines to create countless kilowatts of electricity.
Read More