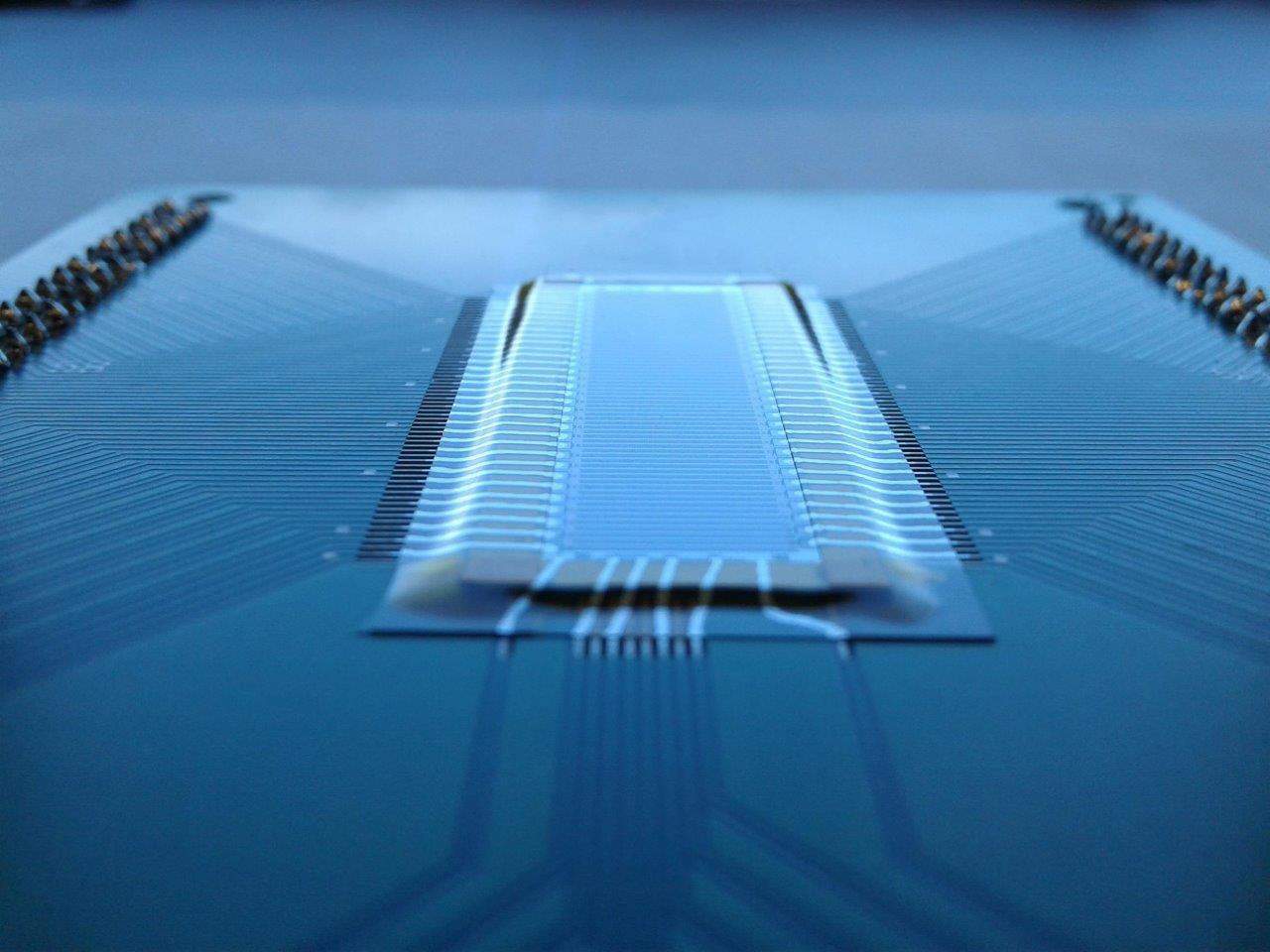
UBC breakthrough opens door to $100 ultrasound machine
Engineers at the University of British Columbia have developed a new ultrasound transducer, or probe, that could dramatically lower the cost of ultrasound scanners to as little as $100. Their patent-pending innovation—no bigger than a Band-Aid—is portable, wearable and can be powered by a smartphone. Conventional ultrasound scanners use piezoelectric crystals to create images of the inside of the body and send them to a computer to create sonograms.
Read More
DARPA Plans a Major Remake of U.S. Electronics
The U.S.Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency is launching a huge expansion of its Electronics Resurgence Initiative, boosting the program to US $1.5 billion over five years. And while some of the research efforts will be just what you’ve come to expect from the agency that brought you disposable drones, self-driving cars, and cameras that can see around corners, a lot of this new money is going toward ideas that could fundamentally change how chips are designed.
Read More
MIT Discovers Way to Mass-Produce Graphene in Large Sheets
The team’s results are the first demonstration of an industrial, scalable method for manufacturing high-quality graphene that is tailored for use in membranes that filter a variety of molecules, including salts, larger ions, proteins, or nanoparticles. Such membranes should be useful for desalination, biological separation, and other applications.
Read More
New lithium-air battery survives hundreds of cycles
Batteries supply electrons by undergoing reversible chemical reactions. That has meant that all the reactants have to be inside the battery, which adds to its weight and volume. Lithium-air batteries could potentially change that situation.
Read More
In field tests, device harvests water from desert air
You really can extract clean drinking water right from the air, even in the driest of deserts, MIT researchers have found. They’ve demonstrated a real-world version of a water-harvesting system based on metal organic frameworks, or MOFs, that they first described last year.
Read More
New study tracks the evolution of stone tools
For at least 2.6 million years, humans and our ancestors have been making stone tools by chipping off flakes of material to produce sharp edges. We think of stone tools as very rudimentary technology, but producing a usable tool without wasting a lot of stone takes skill and knowledge. That’s why archaeologists tend to use the complexity of stone tools as a way to measure the cognitive skills of early humans and the complexity of their cultures and social interactions.
Read More
Is Google Going Underground with Hypersonic Tech?
Google is carrying out research on hypersonics, probably for new technologies to slash the cost of geothermal energy and tunneling. It could also be acquiring a Washington-based startup called HyperSciences that has already built prototype devices.
Read More
Technique to see objects hidden around corners
A driverless car is making its way through a winding neighborhood street, about to make a sharp turn onto a road where a child’s ball has just rolled. Although no person in the car can see that ball, the car stops to avoid it. This is because the car is outfitted with extremely sensitive laser technology that reflects off nearby objects to see around corners.
Read More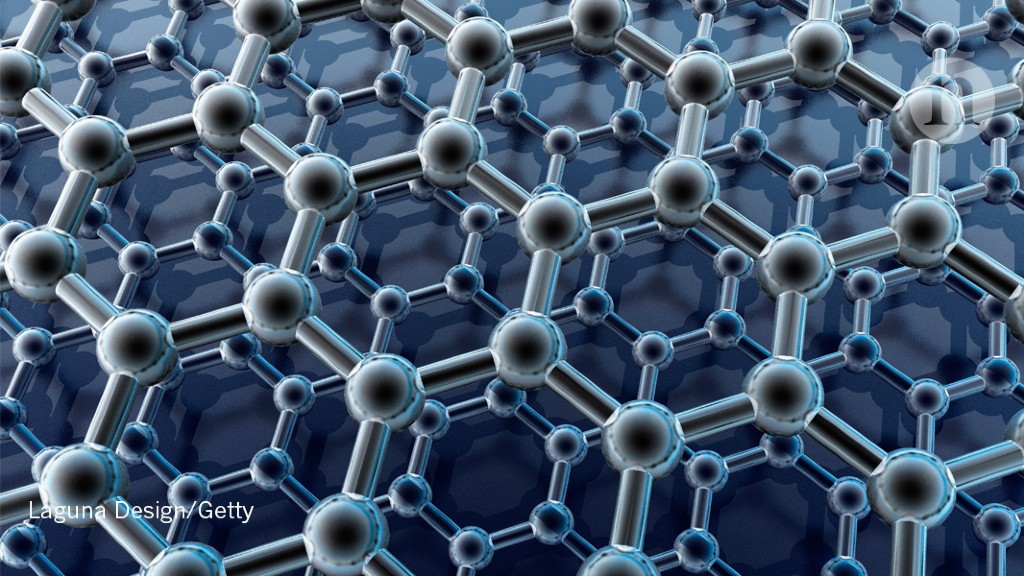
Surprise graphene discovery could unlock secrets of superconductivity
A sandwich of two graphene layers can conduct electrons without resistance if they are twisted at a ‘magic angle’’, physicists have discovered. The finding could prove to be a significant step in the decades-long search for room-temperature superconductors.
Read More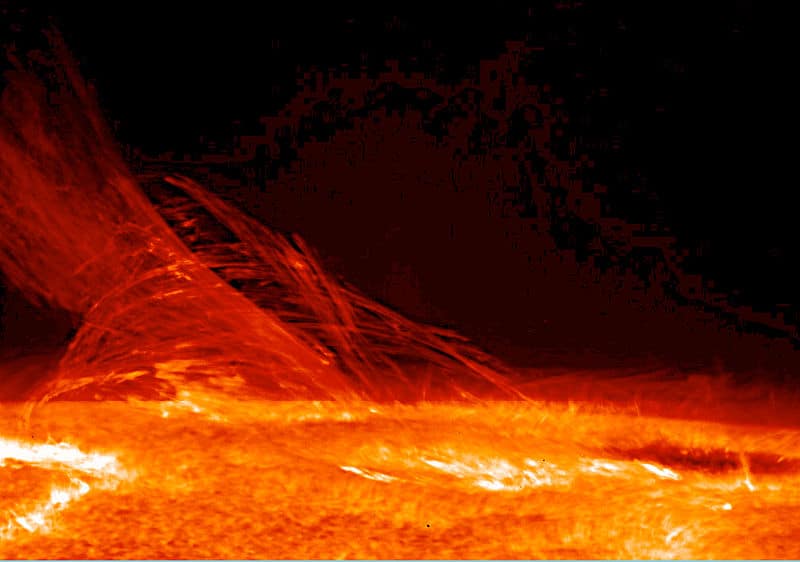
AI Researchers Aim to Crack Code on ‘Sun Energy’
Since the ’50s, scientists have chased the promise of clean energy from sun-like reactions between deuterium and tritium, the plentiful isotopes of hydrogen. This carbon-free energy, achieved at temperatures of 360 million degrees Fahrenheit, would offer a great way to heat water and, in turn, spin turbines to create countless kilowatts of electricity.
Read More
A Preview of Bristlecone, Google’s New Quantum Processor
The goal of the Google Quantum AI lab is to build a quantum computer that can be used to solve real-world problems. Our strategy is to explore near-term applications using systems that are forward compatible to a large-scale universal error-corrected quantum computer. In order for a quantum processor to be able to run algorithms beyond the scope of classical simulations, it requires not only a large number of qubits.
Read More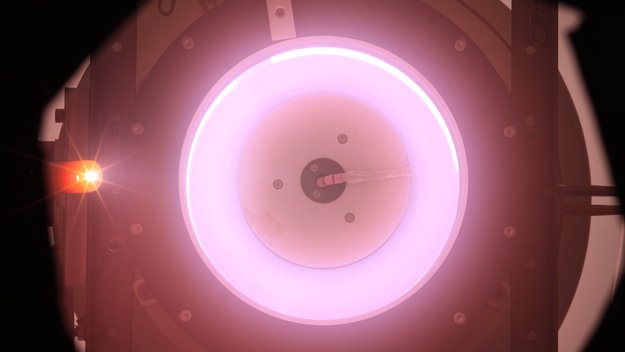
First firing of air-breathing Electric Truster
In a world-first, an ESA-led team has built and fired an electric thruster to ingest scarce air molecules from the top of the atmosphere for propellant, opening the way to satellites flying in very low orbits for years on end.
Read More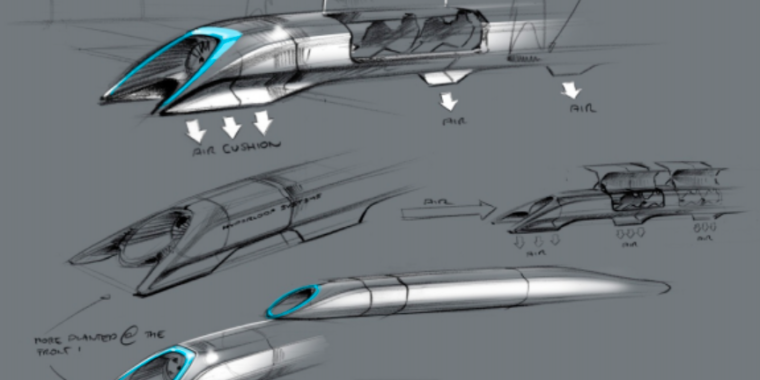
Is it time to take the Hyperloop seriously?
Imagine traveling the length of the United Kingdom—from London to Edinburgh, 400-plus miles—in under an hour. A journey from Los Angeles to San Francisco would take less than 30 minutes (five hours less than the average drive between the two cities). Your journey would be safe and comfortable, your carbon footprint almost non-existent.
Read More
Magic Leap New Patent Applications
Just some quick notes to let my readers know I am in the process of digesting some new Magic Leap Patent Applications that were published last week. There are several related applications, but the most interesting one was US20180052277 MULTI-LAYER DIFFRACTIVE EYEPIECE. This application is 272 pages long, and I have only had time to flip through it, so this is all preliminary information, so I am mostly going off the figures.
Read More
