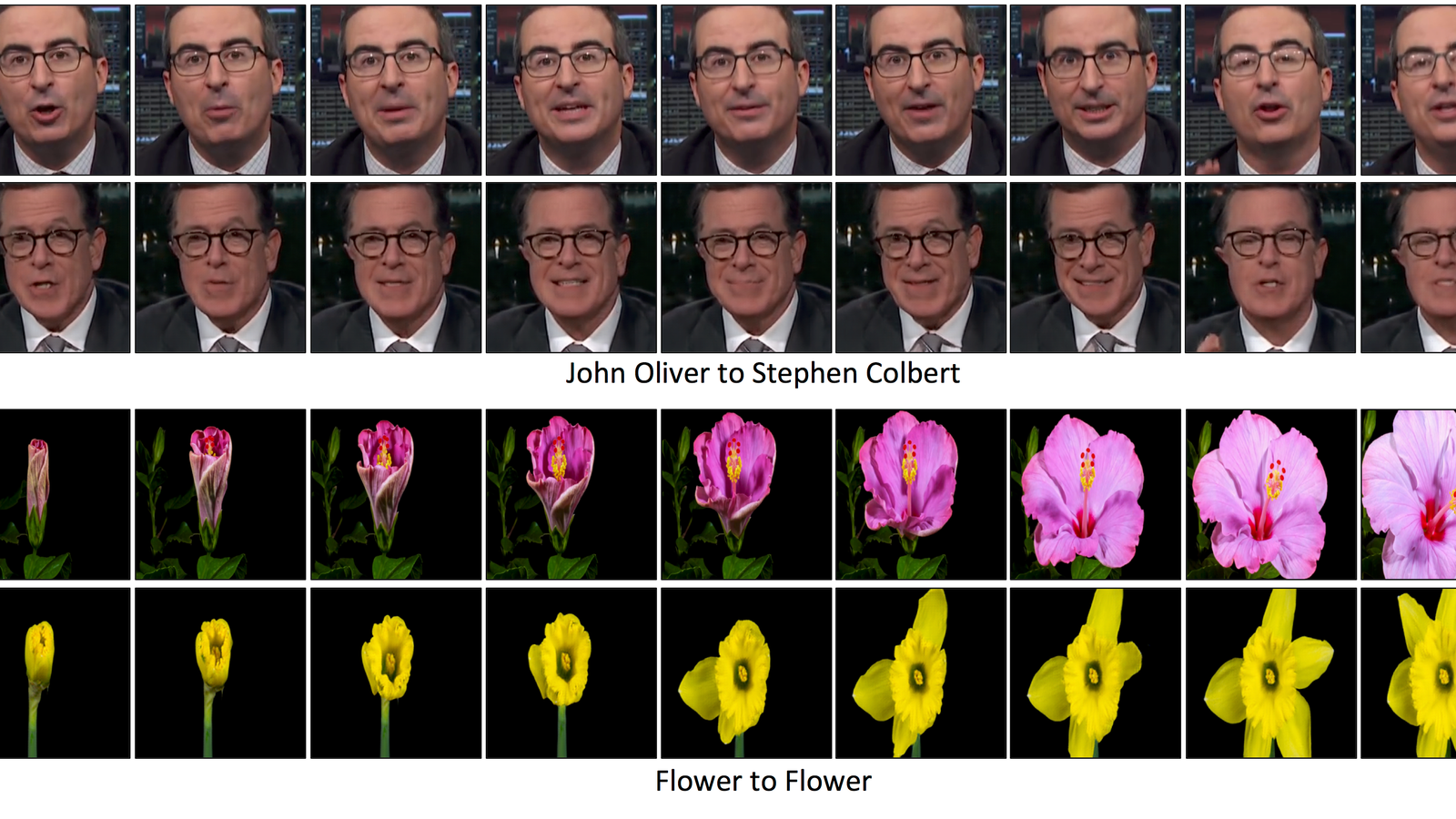
Carnegie Mellon Researchers Develop New Deepfake Method
Deepfakes, ultrarealistic fake videos manipulated using machine learning, are getting pretty convincing. And researchers continue to develop new methods to create these types of videos, for better or, more likely, for worse. The most recent method comes from researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, who have figured out a way to automatically transfer the “style” of one person to another.
Read More
Facebook’s Field Guide to Machine Learning video series
The Facebook Field Guide to Machine Learning is a six-part video series developed by the Facebook ads machine learning team. The series shares best real-world practices and provides practical tips about how to apply machine-learning capabilities to real-world problems. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are in the headlines everywhere today, and there are many resources to teach you about how the algorithms work and demonstrations of the latest cutting-edge research.
Read More
Diving into Deep Convolutional Semantic Segmentation Networks and Deeplab_V3
Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) have achieved remarkable success in various Computer Vision applications. Like others, the task of semantic segmentation is not an exception to this trend.
Read More
Predicting e-sports winners with Machine Learning
Video game/E-sports streaming is a huge and ever rising market. In the world championship of League of Legends (LoL) last year, one semifinal attracted 106 million viewers, even more than the 2018 Super Bowl. Another successful example is Twitch, where thousands of players broadcast their gameplay to millions of viewers.
Read More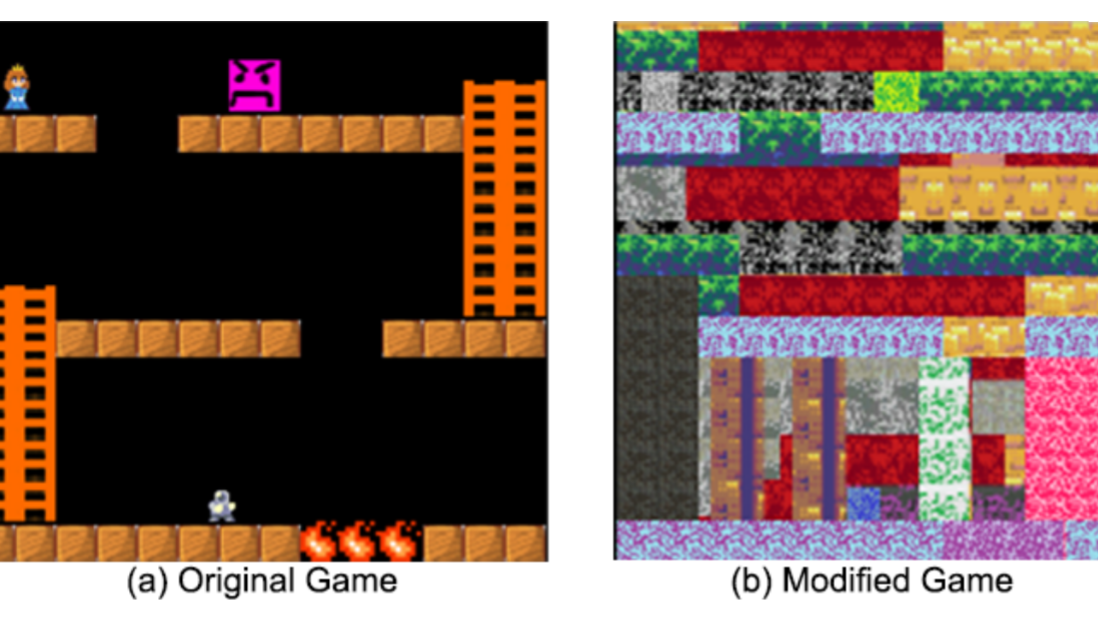
Why humans learn faster than AI for now
In 2013, DeepMind Technologies, then a little-known company, published a groundbreaking paper showing how a neural network could learn to play 1980s video games the way humans do by looking at the screen. These networks then went on to thrash the best human players.
Read More
Open Sourcing the Hunt for Exoplanets
Recently, we discovered two exoplanets by training a neural network to analyze data from NASA’s Kepler space telescope and accurately identify the most promising planet signals. And while this was only an initial analysis of ~700 stars, we consider this a successful proof-of-concept for using machine learning to discover exoplanets, and more generally another example of using machine learning to make meaningful gains in a variety of scientific disciplines (e.g. healthcare, quantum chemistry, and fusion research)
Read More
Reptile: A Scalable Meta-Learning Algorithm
We’ve developed a simple meta-learning algorithm called Reptile which works by repeatedly sampling a task, performing stochastic gradient descent on it, and updating the initial parameters towards the final parameters learned on that task. This method performs as well as MAML, a broadly applicable meta-learning algorithm, while being simpler to implement and more computationally efficient.
Read More
Machine Learning Workflow on Diabetes Data : Part 02
In my last article of this series, we discussed about the machine learning workflow on the diabetes data set. And discussed about topics such as data exploration, data cleaning, feature engineering basics and model selection process. You can find the previous article below.
Read More
This Neural Net Hallucinates Sheep
If you’ve been on the internet today, you’ve probably interacted with a neural network. They’re a type of machine learning algorithm that’s used for everything from language translation to finance modeling. One of their specialties is image recognition.
Read More
“Cracking” Morse code with RNNs
Spoiler alert: Morse code doesn’t really need cracking. Its useful because messages can be sent using this code with minimal equipment, and I say it doesn’t need cracking because the code is well known and what the combinations of dots and dashes stand for is no secret. But, in theory, it is a substitution cipher — where each letter of the alphabet (and each digit) has some representation using dots and dashes, as illustrated below.
Read More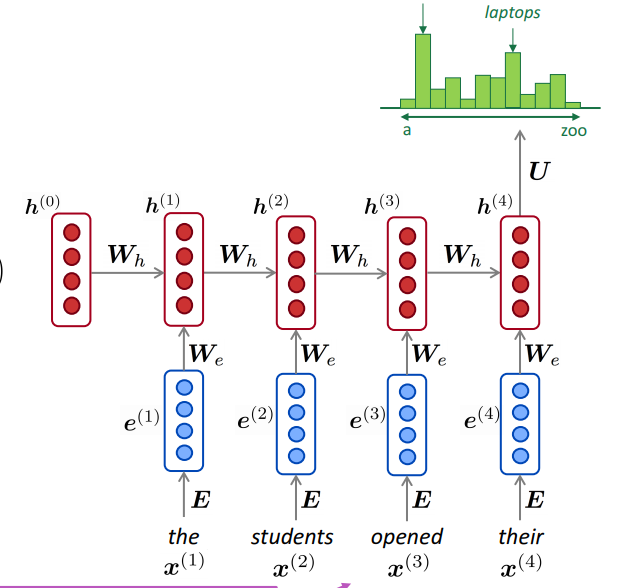
Building a Next Word Predictor in Tensorflow
Next Word Prediction or what is also called Language Modeling is the task of predicting what word comes next. It is one of the fundamental tasks of NLP and has many applications. You might be using it daily when you write texts or emails without realizing it.
Read More
Bonsai AI: Using Simulink for Deep Reinforcement Learning
Simulink provides a great training environment for DRL as it allows 3rd parties like Bonsai to integrate and control simulation models from the outside. This ability is one of the basic requirements for simulation platforms to be feasible for Deep Reinforcement Learning using Bonsai AI. More requirements can be found here.
Read More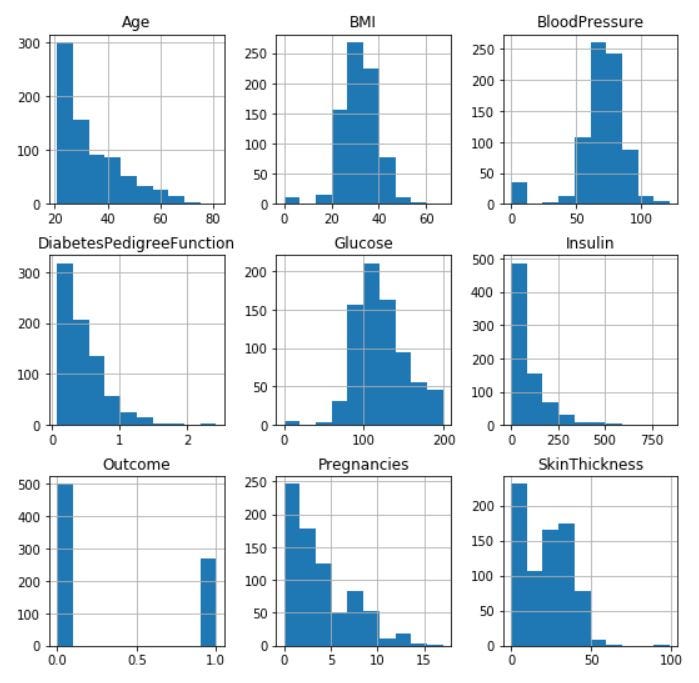
Machine Learning Workflow on Diabetes Data : Part 01
This article will portray how data related to diabetes can be leveraged to predict if a person has diabetes or not. More specifically, this article will focus on how machine learning can be utilized to predict diseases such as diabetes. By the end of this article series you will be able to understand concepts like data exploration, data cleansing, feature selection, model selection, model evaluation and apply them in a practical way.
Read More
So what’s new in AI?
I graduated with a degree in AI when the cost of the equivalent computational power to an iPhone was $50 million. A lot has changed but surprisingly much is still the same.
Read More
Google-Landmarks: A New Dataset and Challenge for Landmark Recognition
A few examples of images from the Google-Landmarks dataset, including landmarks such as Big Ben, Sacre Coeur Basilica, the rock sculpture of Decebalus and the Megyeri Bridge, among others.
Read More
Learning by playing
Our new paper proposes a new learning paradigm called ‘Scheduled Auxiliary Control (SAC-X)’ which seeks to overcome the issue of exploration in control tasks. SAC-X is based on the idea that to learn complex tasks from scratch, an agent has to learn to explore and master a set of basic skills first. Just as a baby must develop coordination and balance before she crawls or walks—providing an agent with internal (auxiliary) goals corresponding to simple skills increases the chance it can understand and perform more complicated tasks.
Read More
Machine Learning Crash Course
How does machine learning differ from traditional programming?What is loss, and how do I measure it?How does gradient descent work?How do I determine whether my model is effective?How do I represent my data so that a program can learn from it?How do I build a deep neural network?
Read More
A Statistical Search for Genomic Truths
The computer scientist Barbara Engelhardt develops machine-learning models and methods to scour human genomes for the elusive causes and mechanisms of disease.
Read More




